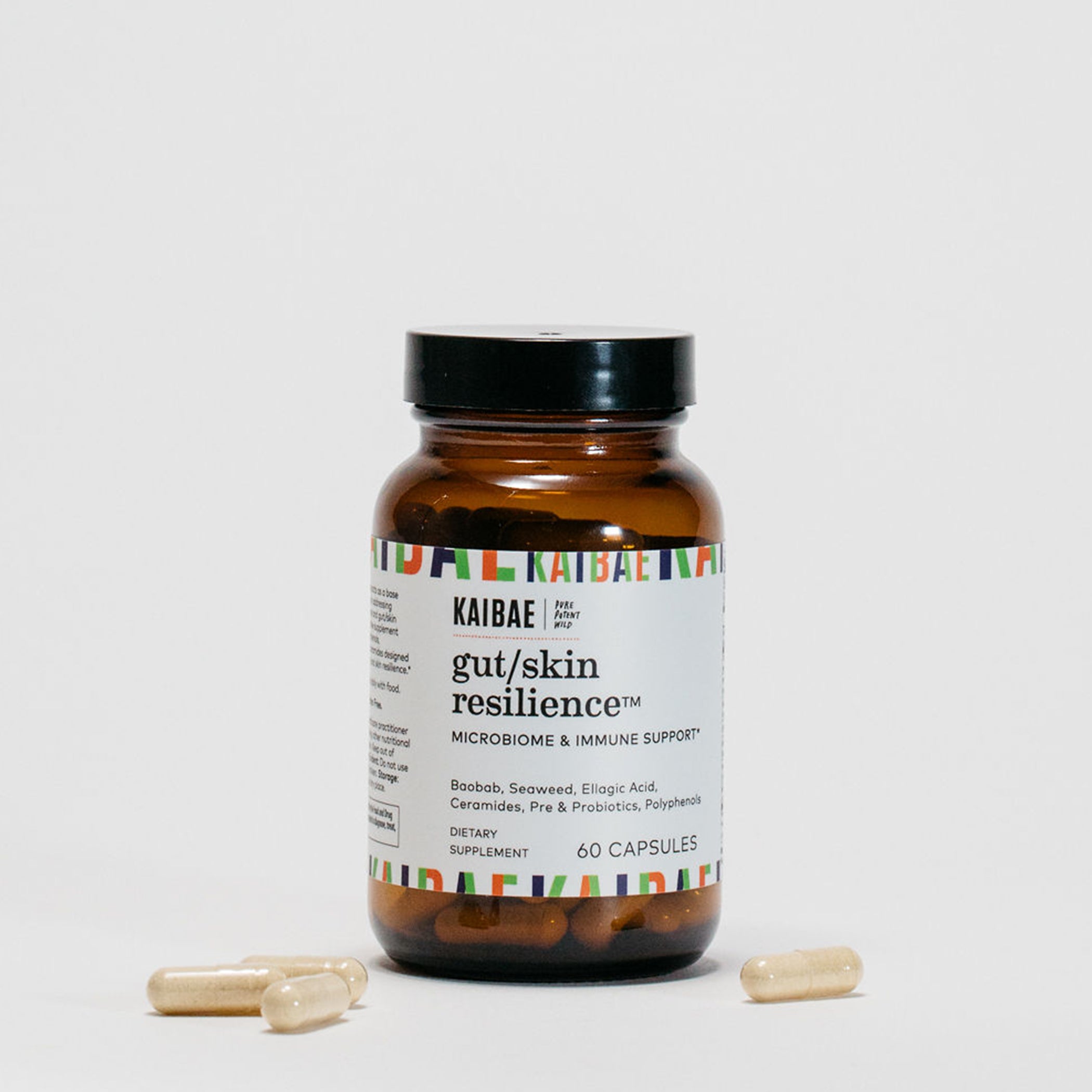
Gut Health
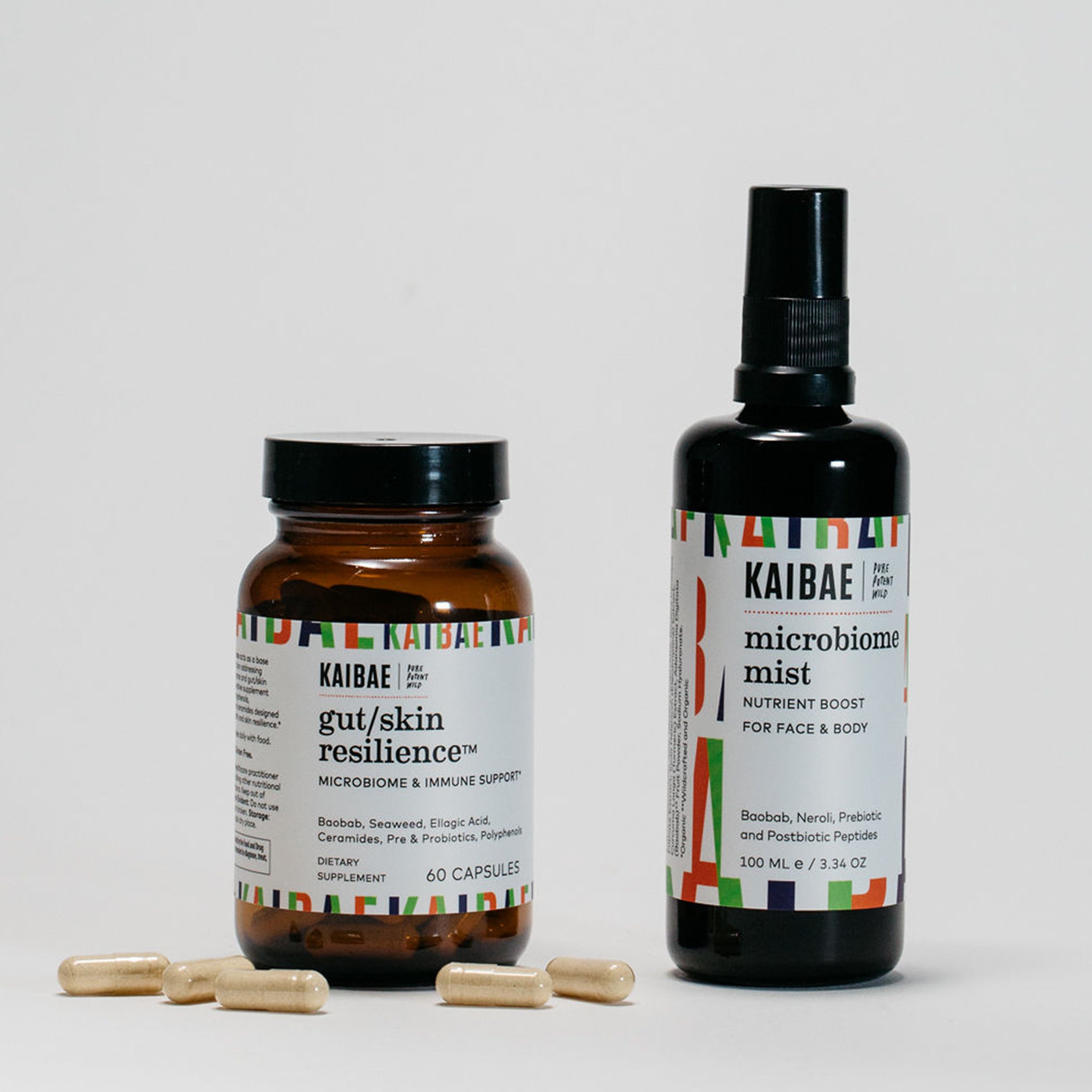
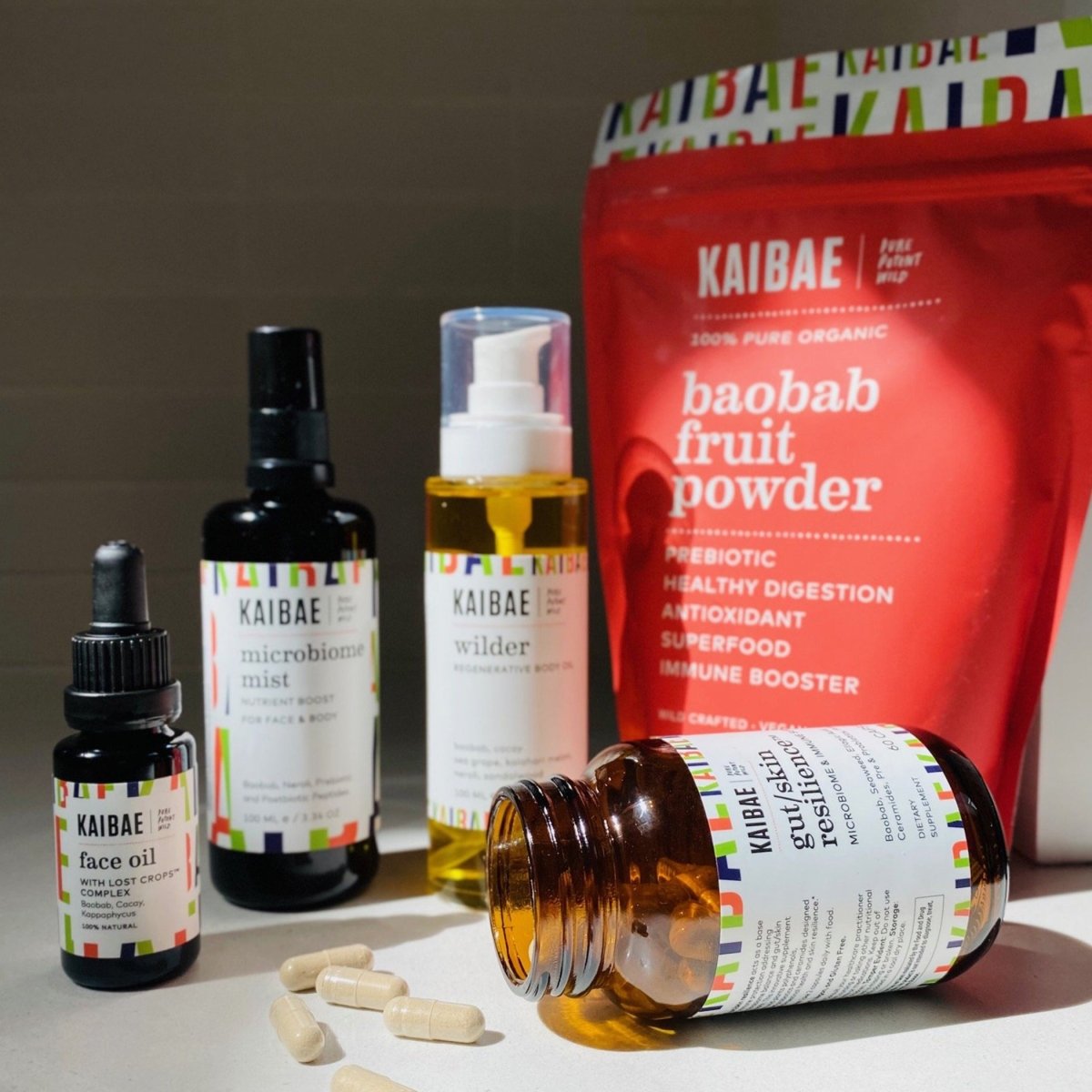
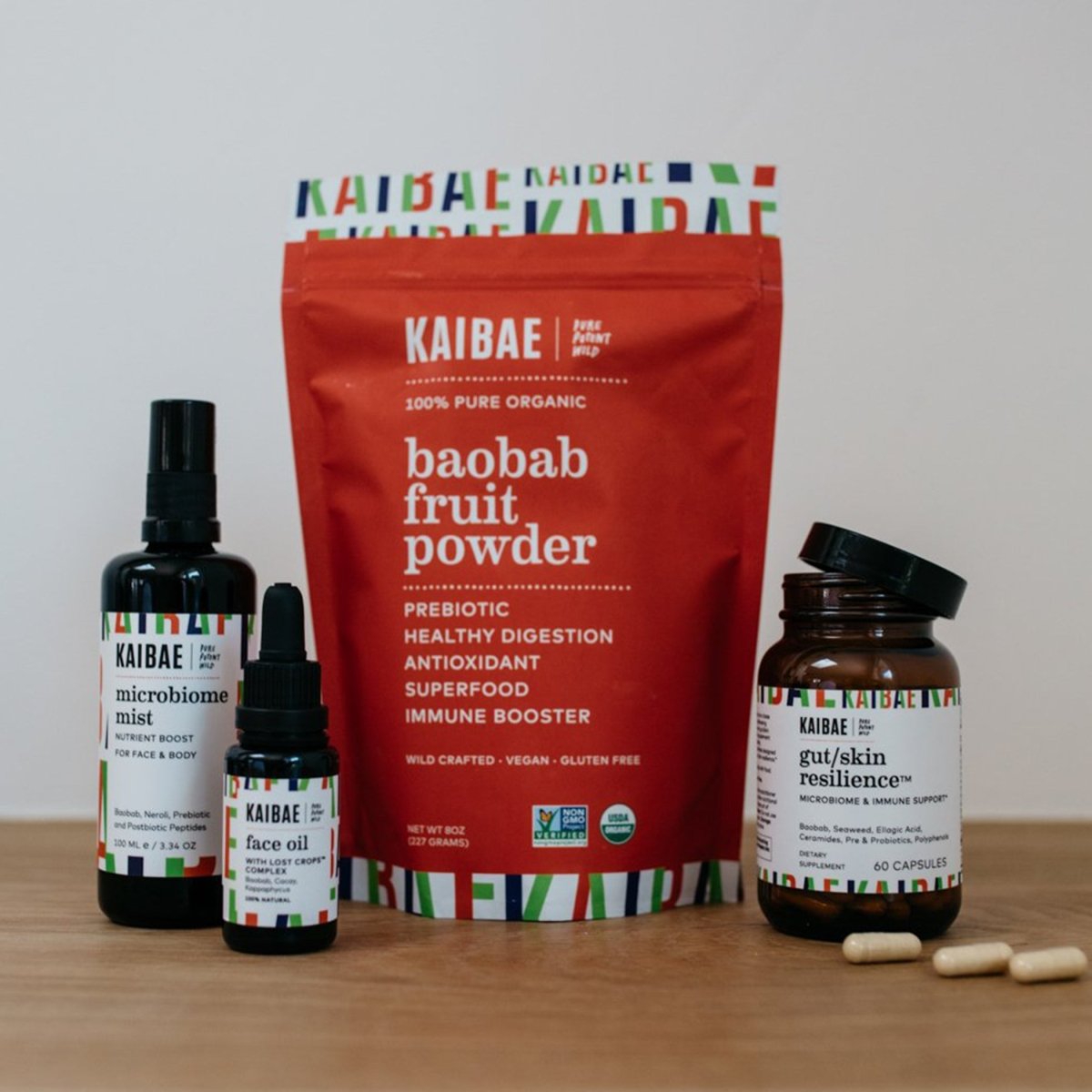
Gut health is essential to all aspect of health. Baobab powder is rich in prebiotic fiber, polyphenols, and vitamin C supporting probiotic balance for healthy digestion immunity, and glowing skin.


baobab powder go sticks


stress resilience


Resilience Series
FAQ's GUT HEALTH
The gut is the foundation of your overall health, as it plays a vital role in digestion, nutrient absorption and waste elimination
Gut health refers to the balance and optimal function of the gastrointestinal tract and the trillions of micro-organisms that make up the gut microbiome..
- Immune system support About 70% of the immune system is located in the gut, making gut health essential for proper immune function and disease prevention.
- Systemic impactA healthy gut affects various bodily systems and can help prevent or manage conditions like autoimmune disorders, heart disease, diabetes, and cancer.
- Mental health The gut produces over 90% of the body's serotonin, a hormone that affects mood and happiness. This gut-brain connection influences mental health and emotional well-being.
- Microbiome balance: Gut health involves a balance between beneficial and potentially harmful bacteria.
70 % of your immune system is in the gut. A balanced gut microbiome produces metabolites that promote immune strength and help reduce inflammation.
Poor gut health can manifest as various symptoms, including digestive issues (like bloating, constipation, or diarrhea), chronic pain, mental health problems, weight gain, migraines, recurrent infections, inflammation, and fatigue.
- Several Neurotransmitters are produced by microorganisms in the gut. Research shows that dysbiosis, an imbalance of microorganisms in the gut contributes to mood disorders. The gut-brain axis describes the bidirectional influence between the gut and the brain.
- Serotonin: Over 90% of the body's serotonin is synthesized in the gut. Various gut bacteria like Streptococcus, Enterococcus, Escherichia, Lactobacillus plantarum, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Morganella morganii have been shown to produce serotonin.
- Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA): Many gut bacteria can produce GABA, including species from the genera Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium, Bacteroides, Parabacteroides, Eubacterium, and Blautia.
- Dopamine: Dopamine is produced in both the central nervous system and the periphery, including the gut. Bacteria such as Lactobacillus and Bacillus species can produce dopamine.
Gut bacteria like Lactobacillus, Bacillus, and Saccharomyces species can produce norepinephrine.
The gut is an important interface between the external environment and our own body. Leaky gut syndrome describes a loss of gut barrier integrity where the tight junctions between cells called enterocytes have become more permeable to bacteria and toxins.